INNOVATING FOR A SUSTAINABLE WATER FUTURE
Along with rapid urbanisation and industrial growth, Asia’s water supply remains susceptible to pollution and climate change. Notorious for on-site leakages and disposal of contaminated wastewater, the industrial sector is responsible for the release of 80% of untreated wastewater into the environment globally. Given that we live in a world where the use of resources might exacerbate the effects of climate change, governments and corporations are prioritising efforts to mitigate the effects of water pollution on the environment – with efficient water management, treatment, reuse and recycling systems.
Singapore’s national water agency, the Public Utilities Board (PUB) is researching on sewage surveillance by sampling used water for pathogens, to detect the presence of viral outbreaks like the COVID-19 pandemic. In Indonesia, the provincial government of Jakarta and the Water Resources Agency has proposed a funding of USD 207 million for the Jakarta Sewerage System (JSS) project to manage domestic waste and water treatment through advanced technologies in 15 city zones.
As the consumer market leans towards a sustainable agenda, the industry is ramping up efforts to improve energy efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of their operations through investments in R&D and adopting a smarter approach for clean water management.
Reducing waste and carbon footprint
Fluence Corporation’s SUBRE tower incorporates the membrane aerated biofilm reactor (MABR) technology to remove waste and biological nutrients from water. The process involves submerging the semi-permeable membrane into a wastewater tank and blowing low-pressure air through the air side of the membrane. Oxygen is constantly supplied to the fixed nitrifying biofilm that develops on the wastewater side of the membrane, while denitrification occurs in the anoxic bulk liquid. Lowering chemical use by 30%, the SUBRE MABR is available as a retrofit upgrade to existing basins, and as a new greenfield solution for custom-built towers. With the capacity to treat up to 757,000 litres of wastewater per day, the system improves effluent water quality, resulting in operational savings, increased capacity and minimal footprint requirements.
Double filtration for maximum security
For drinking water and wastewater treatment, compressed air treatment technologies are crucial. High-efficiency compressors conserve resources and reduce harmful emissions. The BOGE CC-2 oil-water separator is a direct and cost-effective solution for the treatment of oily condensate before releasing to the common drain systems. BOGE, a leading specialist in industrial air compressor systems, developed an oil-water separator system utilising high quality active carbon and polypropylene filters to provide optimum and superior condensate cleaning. With its double filtration process, the syste m effectively removes mineral oil and synthetic coolant residue. The condensate is first discharged through a pressure relief chamber and passed through a polypropylene element, followed by another filtration process in the second chamber to remove any final impurities. The treated water with less than 10 ppm of residual oil content directly discharges into the sewage system for maximum security. Opting for a fuss-free servicing of systems which reduces maintenance and environmental disposal costs, the compressors are designed with replaceable filter elements without the additional step of removing liquid or oil residues from the containers.
m effectively removes mineral oil and synthetic coolant residue. The condensate is first discharged through a pressure relief chamber and passed through a polypropylene element, followed by another filtration process in the second chamber to remove any final impurities. The treated water with less than 10 ppm of residual oil content directly discharges into the sewage system for maximum security. Opting for a fuss-free servicing of systems which reduces maintenance and environmental disposal costs, the compressors are designed with replaceable filter elements without the additional step of removing liquid or oil residues from the containers.
Real-time cloud insights
Arming users with real-time data, tech start-up, WEGoT Utility Solutions’ VenAqua technology addresses the lack of clean water supply and greater incidence of wastewater in residential and commercial sectors by managing demand. WEGoT equips water treatment plants with innovative IoT-enabled ultrasonic sensors to detect leakages and abnormal consumptions like drips and fixture efficiency. Consumption pattern data from a series loop of sensors 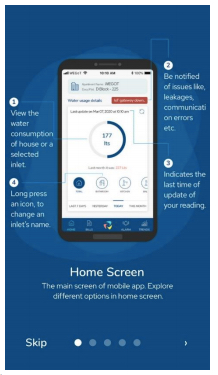 installed in water inlets is transmitted to an accessible WEGoT 3.0 cloud mobile application. Along with minute-wise insights, users also have remote access to shut off open taps and valves when not in use. To date, the start-up has successfully saved more than 1 billion litres of water with sensors installed in over 30,000 homes and 2.79 million sqm of commercial spaces. Last year, the start-up received a seed funding of USD 2 million to enhance its sensor based IoT device and scale up operations in India.
installed in water inlets is transmitted to an accessible WEGoT 3.0 cloud mobile application. Along with minute-wise insights, users also have remote access to shut off open taps and valves when not in use. To date, the start-up has successfully saved more than 1 billion litres of water with sensors installed in over 30,000 homes and 2.79 million sqm of commercial spaces. Last year, the start-up received a seed funding of USD 2 million to enhance its sensor based IoT device and scale up operations in India.
Drivers of change
The future of urban water is influenced by many factors including water scarcity, urban population growth and necessity for efficient systems. Asia’s cities will have to focus on local water sourcing, reuse and recycling to sustain their populations. An early response to increasing energy and resources through the development of efficient processes and smarter systems is key. Increasing investments in green infrastructure offers the opportunity to access and directly treat new and underutilised water sources.






